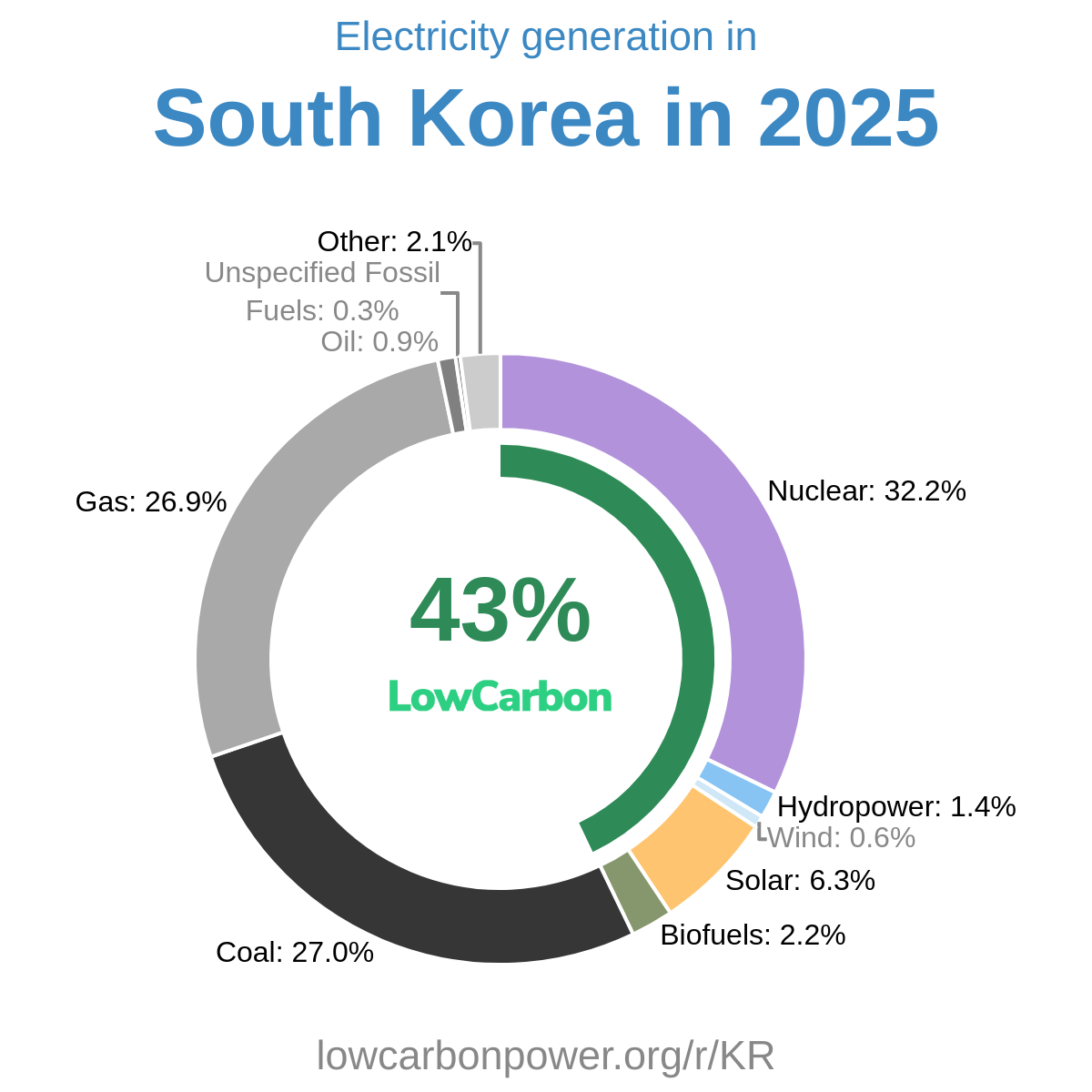
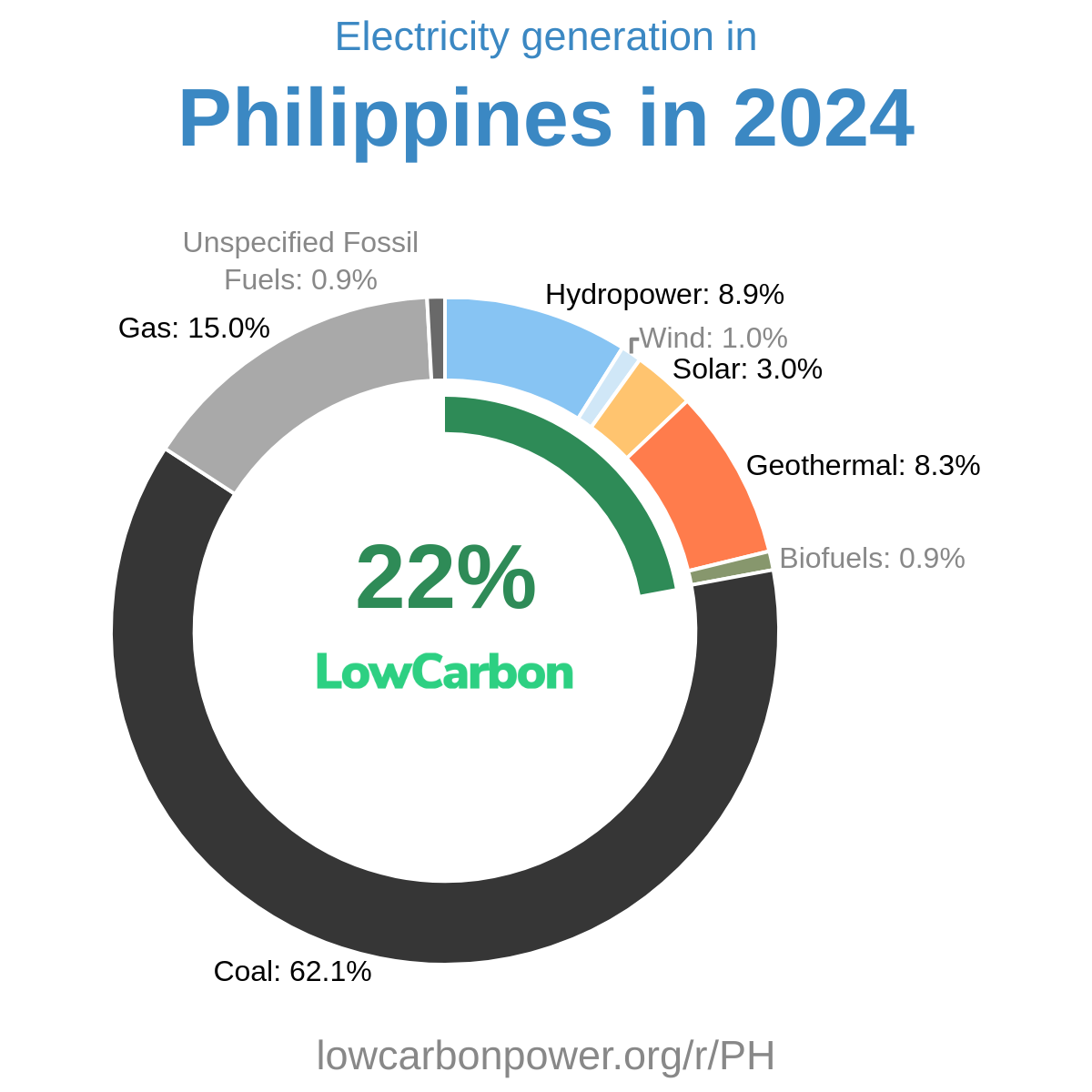
In 2022, electricity consumption in Malawi was characterized by a significant reliance on low-carbon sources, with nearly all of its electricity coming from hydropower, which contributed around 1.7 TWh, and even a touch of biofuels rounding out the total to 1.75 TWh. This commitment to low-carbon electricity is commendable, yet, in terms of overall consumption, Malawi finds itself lagging far behind the global average, with just 89 kWh consumed per person compared to the global average of 3658 kWh/person. This stark difference points to possible consequences such as limited industrial growth, educational challenges due to unreliable power, and overall economic stagnation, potentially delaying advancements that electrification can nurture.
Data sources used on this page include EIA, Ember and Enerdata. More about data sources →
Is Electricity Growing in Malawi?
Unfortunately, the growth of electricity consumption in Malawi exhibits a concerning downward trend. The most recent consumption figure of 89 kWh/person marks a noticeable decrease from its previous peak of 131 kWh/person in 2014. This decrease of 42 kWh/person reflects a broader sectoral decline, as low-carbon electricity generation also fell from its previous apex of 123 kWh/person down to 85 kWh/person—a drop of 38 kWh/person. Such regressions in both total and low-carbon electricity usage are alarming, as they signify stagnation at a time when the global community is racing towards sustainable electrification and modernization.
Suggestions
To boost low-carbon electricity generation, Malawi can draw valuable lessons from various regions that have successfully harnessed solar and nuclear energy. Notably, India has made significant strides in solar power, generating 162 TWh, which could inspire Malawi to capitalize on its abundant sunlight. Similarly, lessons from Brazil's wind energy development, with 106 TWh, indicate potential for diversification into wind energy that Malawi could explore. Nuclear energy, employed effectively by countries like France and the United States, with productions of 371 TWh and 778 TWh respectively, offers a scalable, reliable option for sustained electricity supply, providing a lucrative avenue to achieve energy independence and mitigate climate-related challenges.
History
Looking back at Malawi's history of low-carbon electricity generation, the primary focus has been hydropower, showing small but steady increases throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, with gains of about 0.1 TWh in the years 1992, 1997, 1998, and sporadically thereafter. Notable surges were seen in 2010 with a 0.3 TWh boost. However, troubling signs appeared in 2017 and 2018 with declines of 0.1 TWh and 0.4 TWh, indicating vulnerabilities within the existing infrastructure that need addressing. While solar energy was introduced in 2018, further commitment and investment could cement it as a cornerstone of Malawi’s energy future, enabling capacity building and energy security. This historical analysis underscores the necessity for proactive steps to expand and diversify Malawi's green electricity portfolio, especially centering on robust, clean technologies like nuclear and solar power.